Crafting Stories on Screen: The Evolution of Narrative Cinema
Trace the evolution of narrative cinema from its early silent film roots to today's digital storytelling innovations in film
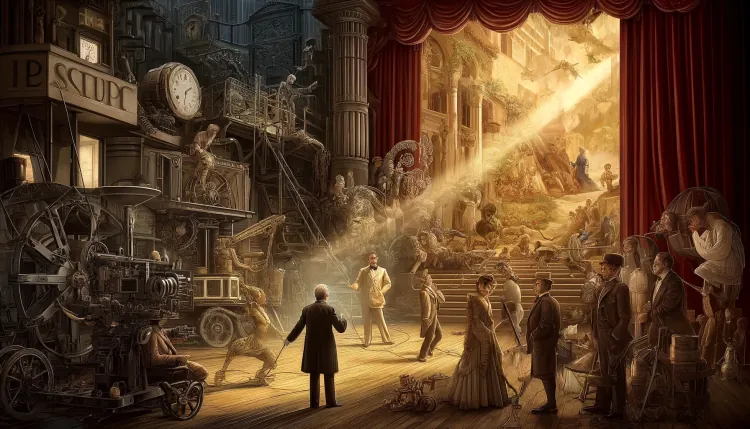

-
Introduction
- Overview of the significance of narrative cinema in the evolution of film.
-
Early Experiments and Pioneers
- Initial non-narrative films and the transition to storytelling.
- Georges Méliès's contributions with "A Trip to the Moon."
-
The Birth of a Language
- Development of film language: editing, continuity, and cinematic techniques.
- D.W. Griffith’s influence and contributions, despite the controversies.
-
The Establishment of Genre and Style
- The crystallization of genres: westerns, comedies, gangster films.
- Influence of film movements like German Expressionism on narrative.
-
Sound and Dialogue
- The transition from silent to sound films.
- Impact of "The Jazz Singer" and the integration of dialogue in storytelling.
-
Global Narratives and New Waves
- Post-WWII cinema and the reflection of local cultures and issues.
- Impact of New Waves on narrative cinema: French, Japanese, Brazilian.
-
Modern Narrative Techniques
- The influence of digital technology and global storytelling methods.
- The role of streaming platforms in shaping long-form narrative content.
-
Conclusion
- The continuous evolution of narrative cinema as a dynamic art form.
-
FAQs
- How did narrative cinema develop?
- What impact did sound have on film storytelling?
- What are key films that shaped narrative cinema?
Introduction Narrative cinema, a crucial aspect of film history, has transformed dramatically from the earliest days of motion pictures. This evolution has not only revolutionized visual storytelling but also turned cinema into a pivotal medium for cultural expression and artistic innovation.
Early Experiments and Pioneers Initially, films were mere recordings of everyday events without narrative structure. Georges Méliès, a visionary filmmaker, transitioned cinema from these "actualities" to stories filled with imagination and fantasy, most notably in his groundbreaking 1902 film, "A Trip to the Moon." Méliès’s work showcased cinema’s potential for narrative, setting the stage for its future development.
The Birth of a Language As films grew in length and complexity, a coherent narrative language began to form. Filmmakers experimented with techniques like continuity editing and cross-cutting to craft compelling stories. D.W. Griffith's films, such as "The Birth of a Nation," though controversial, were instrumental in refining these techniques, offering new ways to convey narrative depth and emotional resonance.
The Establishment of Genre and Style By the 1920s and 1930s, distinct film genres and stylistic conventions had emerged. This era solidified styles such as the western and gangster film, each with its own narrative approach. Simultaneously, German Expressionism brought a visual intensity to storytelling, influencing filmmakers worldwide with its stylized aesthetics.
Sound and Dialogue The advent of synchronized sound revolutionized narrative cinema. "The Jazz Singer" introduced audiences to the power of spoken dialogue, enriching storytelling possibilities and leading to more intricate narratives. Sound films allowed for a greater exploration of themes and character development, deepening the cinematic experience.
Global Narratives and New Waves After World War II, global cinema began reflecting more diverse stories and perspectives. Italian Neorealism, for example, portrayed the struggles of ordinary people, influencing narrative approaches globally. The various New Waves of the 1950s and 1960s introduced innovative storytelling techniques that challenged traditional narratives and aesthetics.
Modern Narrative Techniques In the modern era, digital technology has further diversified narrative techniques, enabling filmmakers to use non-linear storytelling and interactive formats like virtual reality. Streaming platforms have also reshaped narratives, allowing for more complex, long-form storytelling that extends beyond traditional film formats.
Conclusion Narrative cinema continues to evolve, embracing new technologies and ideas to tell stories that resonate with global audiences. Its development reflects the ongoing potential of film as a form of artistic expression and cultural dialogue.
FAQs
- How did narrative cinema develop?
- Narrative cinema evolved through innovations in film techniques and storytelling, starting with early silent films and advancing through the introduction of sound and digital technologies.
- What impact did sound have on film storytelling?
- Sound transformed narrative cinema by enabling dialogue and auditory elements that enhanced emotional depth and thematic complexity.
- What are key films that shaped narrative cinema?
- Films like "A Trip to the Moon," "The Birth of a Nation," and "The Jazz Singer" were pivotal in developing the narrative capabilities of cinema.
For further exploration of narrative cinema's fascinating journey and its impact on global culture, visit Kiksee Magazine.
What's Your Reaction?