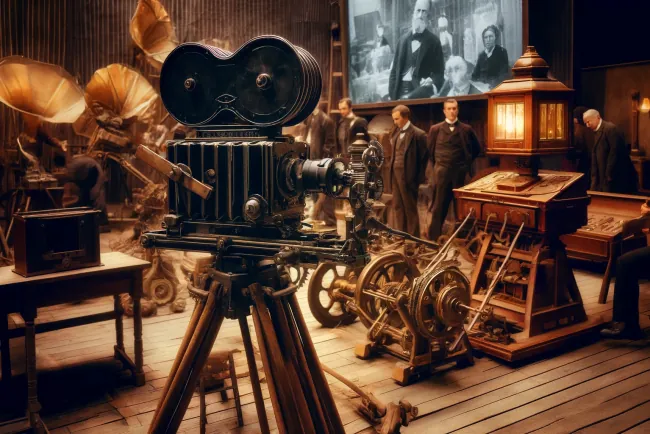
The Silent Film Era: The Dawn of Cinematic Expression
Delve into the Silent Film Era, a time of innovation and iconic stars that shaped the foundational techniques of cinema

-
Introduction
- Overview of the Silent Film Era and its significance in film history.
-
The Beginning of Silent Cinema
- Early motion picture technology by Edison and the Lumière brothers.
- Evolution from short scenes to more complex narratives.
-
The Development of Narrative Cinema
- George Méliès and the introduction of story-driven films.
- Iconic films like "A Trip to the Moon."
-
Rise of Hollywood and the Star System
- Migration of the film industry to Hollywood.
- Emergence of the star system with figures like Charlie Chaplin and Mary Pickford.
-
Technical Innovations
- Introduction of cinematic techniques: close-ups, cross-cutting, special effects.
- Influential films by D.W. Griffith and their impact on editing and narrative.
-
Genre and International Influence
- Development of film genres: horror, westerns, science fiction.
- Contributions from international cinema, notably German Expressionism and Soviet montage.
-
The Transition to Sound
- The end of the Silent Era with the advent of "talkies."
- "The Jazz Singer" and the transformation of the film industry.
-
Legacy
- The enduring impact of the Silent Film Era on modern cinema.
- Study and appreciation of silent films in contemporary culture.
-
Conclusion
- Recap of the Silent Film Era's contributions to the art and technology of filmmaking.
-
FAQs
- Why did the Silent Film Era end?
- How did silent films influence modern cinema?
- What are some must-watch silent films?
Introduction The Silent Film Era, spanning the late 19th century to the late 1920s, marks a revolutionary period in cinema that laid the groundwork for modern filmmaking. This era explored the power of visual storytelling and saw the birth of the film industry as we know it today.
The Beginning of Silent Cinema Inventors like Thomas Edison and the Lumière brothers pioneered early motion picture technologies, capturing brief moments of life that mesmerized viewers. Films during this period evolved from mere novelty acts to captivating narratives that communicated complex stories and emotions.
The Development of Narrative Cinema George Méliès, a magician turned filmmaker, transformed cinema into a medium for fantastical storytelling, best exemplified by his 1902 masterpiece, "A Trip to the Moon." Méliès' innovations in narrative and special effects laid the foundation for genres that would captivate audiences for decades.
Rise of Hollywood and the Star System Hollywood's favorable climate and diverse landscapes made it an ideal hub for film production. Icons like Charlie Chaplin and Mary Pickford rose to fame, shaping the star system that fueled Hollywood's growth and global appeal. Chaplin’s "The Tramp" became an enduring symbol of the Silent Film Era.
Technical Innovations This era witnessed significant technical advancements such as the use of close-ups and innovative editing techniques. Films like "The Birth of a Nation," despite their controversial content, demonstrated the potential of film to create expansive and emotionally compelling narratives.
Genre and International Influence The Silent Film Era was instrumental in the creation of enduring film genres and saw contributions from around the world. German Expressionist films and Soviet films like "Battleship Potemkin" influenced global cinema with their unique styles and narrative techniques.
The Transition to Sound "The Jazz Singer" in 1927 marked a pivotal moment with its synchronized sound, signaling the end of the Silent Film Era. The film industry rapidly adapted to sound, leaving silent films as a nostalgic reminder of cinema's early days.
Legacy Today, the Silent Film Era is celebrated for its pioneering techniques and storytelling. The era's films continue to be studied for their artistic merit and innovation, offering insights into the nascent stages of cinematic expression.
Conclusion The Silent Film Era established many of the conventions still used in cinema today. It remains a testament to the ingenuity of early filmmakers and their enduring influence on the art of filmmaking.
FAQs
- Why did the Silent Film Era end?
- The introduction of synchronized sound and the massive popularity of "talkies" made silent films obsolete.
- How did silent films influence modern cinema?
- Silent films developed essential cinematic techniques, such as the use of visual metaphor and narrative pacing, that continue to influence filmmaking.
- What are some must-watch silent films?
- Classics like "Metropolis," "The General," and "Nosferatu" remain influential and are essential viewing for film enthusiasts.
For more insights into the fascinating world of films, visit Kiksee Magazine.
What's Your Reaction?